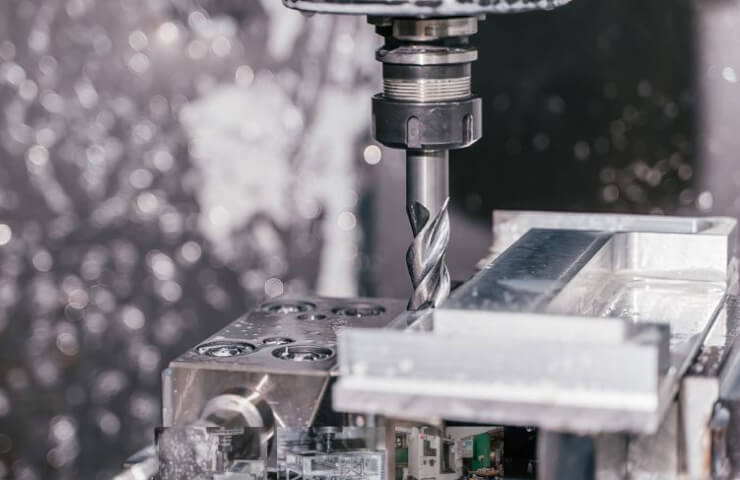
The machinability of metals depends on several factors, each of which must be taken into account in the process of CNC milling on machine tools.
Steel
Machinability of steel is affected by:
-
composition of alloying substances,
-
heat treatment method,
-
Method of obtaining the workpiece.
Possible problems depending on the degree of hardness:
-
Formation of build-ups and burrs in steels with a low carbon content;
-
Cutting edge chipping for high hardness steels.
To prevent the occurrence of these problems, it is important to strictly comply with the requirements for the relative position of the cutter and the workpiece, as well as the reasonable use of cutting fluid.
Stainless steel
-
Ferritic - similar in properties to low carbon steel, so when working with it, you should be guided by the recommendations indicated above for low carbon steel.
-
Martensitic - has a tendency to harden at the moment of cutting, therefore, it requires a higher cutting speed and the most accurate tool path when processing.
-
Austenitic and duplex - they are characterized by the problem of chipping the edge of the cutting tool due to thermal cracks and sticking metal. Parts in this case may have burrs and poor surface finish. In the case of roughing, the recommendations to prevent these disadvantages are as follows: select a high cutting speed to eliminate the sticky material problem and avoid the use of cutting fluid to reduce the likelihood of thermal cracks. For flawless finishing, oil mist or film coolant is recommended (the temperature is lower, so the risk of cracking is not as high as in roughing).
Cast iron
As with steel, there is a lot in CNC milling cast iron depends on its specific alloy.
-
Grey cast iron (GCI) - among the wear defects, abrasive flank wear and thermal cracks can be noted. Parts show chipping. Dry running is recommended to minimize the chance of cracking. Use thicker coated carbide inserts. If there is a problem with chipping of the workpiece metal, check the degree of wear on the flank surface, the thickness of the chips (reduce the feed to reduce it). Try to ensure a high cutting speed and control the appearance of burrs on the workpiece - they slow down the cut.
-
Nodular cast iron (NCI) - has similar processing parameters to those that are relevant for steel. Therefore, the recommendations will be the same. The use of PVD-coated alloys and cutting fluid will achieve optimum results.
-
Compact Graphite Cast Iron (CGI) - choose cutters in accordance with the recommendations relevant for gray cast iron, but separately it makes sense to use inserts with sharper geometry, this will avoid the appearance of burrs on blanks.