Industrial generators are key elements in ensuring continuous power supply in enterprises of various sizes. They play an important role in maintaining stable equipment operation and preventing downtime, which is especially critical in environments with high productivity requirements. Industrial generators are used in a wide range of applications, from plants and factories to construction sites and medical facilities.
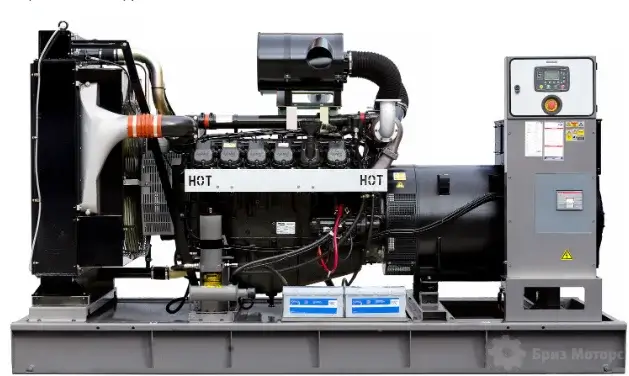
The main functions that an industrial generator performs include generating electrical energy to power various devices and equipment, as well as providing backup power. in case of main network outage. One of the most popular types of such devices is 700 kW diesel generator set , which is characterized by high power and reliability.
Types of industrial generators
Industrial generators are divided into several types depending on the fuel used and the principle of operation:
- Diesel generators:
- Reliability and durability.
- High efficiency under intensive operating conditions.
- Use in facilities with high energy needs.
- /ul>
- Gas generators:
- Efficiency and environmental friendliness.
- Use of natural gas or biogas.
- Suitable for facilities with constant load.
- Gasoline generators:
- Lightness and mobility.
- Used for temporary power supply or at remote sites.
- Shorter service life compared to diesel and gas analogues.
Principles of operation of industrial generators
An industrial generator is a device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. This process includes several stages:
- Mechanical energy: The internal combustion engine (diesel, gas or gasoline) rotates the generator shaft.
- Electromagnetic induction: The rotation of the shaft creates an electromagnetic field, which induces a current in the stator windings.
- Energy conversion: The induced current is converted into electrical energy suitable for powering various consumers.
The main components of an industrial generator are:
- Engine: The heart of the generator, providing mechanical energy.
- Alternator: A device that converts mechanical energy into electrical energy.
- Control system: Provides monitoring and control of the generator.
- Cooling system: Maintains the optimal operating temperature of the generator.
- Exhaust system: Removes exhaust gases, ensuring safe operation.
Advantages of using industrial generators
The use of industrial generators has a number of advantages, including:
- Reliability: Industrial generators provide uninterrupted power supply even in the most extreme conditions.
- Autonomy: They can work independent of the main network, which is especially important in remote or hard-to-reach areas.
- Flexibility: Generators can be used for both main and backup power supply, making them versatile for a variety of applications.
Application of Industrial Generators
Industrial generators are widely used in various industries, including:
- Industrial plants: Providing power to production lines and equipment.
- Construction sites: Powering construction equipment and temporary offices.
- Healthcare facilities: Keeping critical medical equipment running in the event of a main network outage.
- Telecommunications companies: Maintaining base stations and server rooms.
Features of maintenance and operation
To ensure reliable and durable operation of industrial generators, it is necessary to carry out regular maintenance. Includes:
- Oil check and change: Regular oil changes keep the engine running smoothly and prevent engine wear.
- Filter cleaning and replacement: Keep air and fuel filters clean to ensure optimal performance.
- Checking the Cooling System: Maintaining proper coolant levels prevents engine overheating.
- Checking Electrical Connections: Ensuring that all electrical connections are in good contact prevents wasted energy and possible failures.
Conclusions
Industrial generators are an integral part of many modern enterprises, providing reliable and uninterrupted power supply in various conditions. Their choice depends on specific requirements and operating conditions. Regular maintenance and proper operation of generators are key to ensuring their longevity.