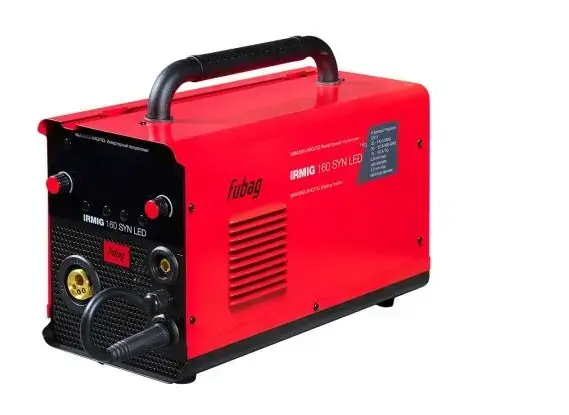
The welding mode determines a set of technical characteristics that affect the quality and efficiency of the welding process. These characteristics include current strength, arc voltage, wire feed rate, connection polarity, and many other parameters. The correct selection of the mode guarantees a reliable seam, the absence of defects and economical energy consumption.
Each material has unique properties such as thermal conductivity, electrical conductivity, chemical activity, and plasticity. That is why the welding mode is selected individually for each specific situation.
For example, steel and aluminum require fundamentally different approaches to welding equipment settings. Cast iron and stainless steel need special modes due to the low thermal conductivity and fragility of the structure, respectively.
The main types of metals and the corresponding welding modes
Let's take a closer look at common metals and suitable welding modes for them.
1. Carbon steel
Carbon steels are characterized by their ease of processing and wide application in construction and mechanical engineering. For welding carbon steels, the MIG/MAG method (metal in a gaseous medium) is most often used.
Recommended mode:
- Current: 120-200 A
- Voltage: 20-25V
- Wire feed speed: 5-10 m/min
- Gas mixture: CO? + Ar (to increase arc stability)
The optimal settings depend on the thickness of the material and the required depth of seam penetration.
Hint: For thin sheets, choose lower values of current and voltage to avoid burning the material.
2. Stainless steel
Stainless steels are characterized by high chromium and nickel content, which makes them resistant to corrosion and aggressive environments. Due to its high resistance to heat, this metal requires special attention when selecting the welding mode.
Recommended mode:
- Current: 80-150 A
- Voltage: 18-22V
- Wire feed speed: 4-8 m/min
- Gas medium: pure Argon (Ar)
Use the minimum possible current value to reduce heat input and deformation of the workpiece.
3. Aluminum and aluminum alloys
Aluminum materials are widely used in the aviation industry, shipbuilding and automotive industries. The features of aluminum are its high thermal and electrical conductivity, which complicates welding.
Recommended mode:
- Current: 150-300 A
- Voltage: 22-28V
- Wire feed rate: 6-12 m/min
- Gas medium: Argon (Ar)
Pay special attention to the cleanliness of the aluminum surface before welding, as the oxide film reduces the adhesive properties of the material.
4. Brass and bronze
Non-ferrous metals such as brass and bronze,