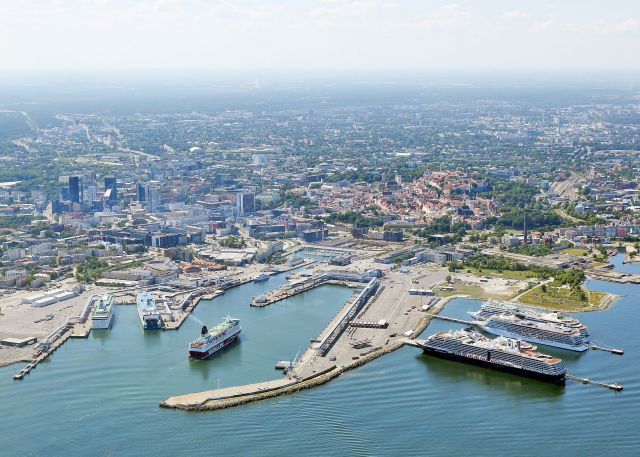
The port plans to build hydrogen storage facilities with a capacity of 25 thousand cubic meters in the Paldiski South Harbor in order to import and export hydrogen in the Baltic region. There are currently no hydrogen terminals in the Gulf of Finland, the port administration said.
This area is suitable for the creation of offshore wind farms, the port administration believes. The electricity generated by the wind turbines can be used to produce green hydrogen, which in turn can serve as bunker fuel, especially for ferries and cruise ships.
In addition to storage facilities, the Port of Tallinn will create the necessary infrastructure for the export and import of green hydrogen. These operations can be carried out through the largest cargo port in Estonia, Muuga, located nearby.
Green hydrogen is one of the leading carbon neutral bunker fuels that can be burned or used to produce green ammonia. Green hydrogen is produced by electrolysis of water using renewable energy. Green ammonia is made by adding nitrogen to green hydrogen.
The World Bank has expressed support for the use of hydrogen as a marine fuel. Many major hydrogen projects have been announced this year.